The refresh rate is the maximum number of frames a monitor can display per second. On the other hand, frame rate means the number of image frames the GPU sends to the monitor per second.This is where confusion begins for most readers. The above definition may not make much sense if you are completely new to the topics, refresh rate, and frame rate. This article explains both the topics and their differences in further detail.
What is a Refresh Rate?
Before we jump into the definition of refresh rate, first, you should know how LED lights on a monitor work. A computer sends data from the frame buffer to the monitor. This data, generated by the CPU or the GPU, contains the stream of pixel color information.Your monitor sets the RGB details(Red, Green, and Blue) for each pixel using the data received from the PC. Once the video data changes, the monitor will also need to refresh and adjust RGB on each pixel.In technical terms, the number of times a single pixel can refresh its RGB intensity in one second is a pixel’s refresh rate. In simpler terms, the refresh rate is the number of times a monitor can refresh an image per second. A refresh rate of a monitor is measured in Hertz. For example, let us consider a monitor with 60 Hz. This monitor can display up to 60 frames in one second. However, this number also depends on your system’s GPU. The monitor, although 60Hz, will not be able to refresh 60 frames in a second if your system’s GPU is not powerful enough to supply 60 frames in a second. However, if a powerful GPU can supply more than 60 frames, say 144 frames in a second. The monitor, being limited to 60 Hz, can only display 60 frames. Here, the monitor cannot show the remaining 84 (144-60) frames.
What is a Frame Rate?
Before we talk about frame rates, it is imperative that you know how a computer processes images. The CPU sends data to the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), which processes this data and generates a series of still images.Every still image is called a frame which consists of information for the display unit as to how the pixels need to light up. The brightness of the pixels, the color of an individual pixel, and so on.The GPU then sends frames to the monitor per second. The monitor then displays these frames one after another, creating a visual output. Several fast-changing frames of images are played to create a sense of motion on the screen of the display unit.Frame rate or Frames Per Second (FPS) is the number of frames that the GPU sends to the monitor. The frame rate entirely depends on how powerful of a GPU you have and the amount an application generates. Most video files play 24FPS. This means that the monitor is displaying 24 images in one second, creating an illusion of objects moving. Certain games or applications are known to support high FPS, ranging from 60FPS to a massive 200+FPS, giving a seamless transition for the changing objects.If you are using a system with a powerful GPU, it will be able to generate more frames per second. However, as discussed above, you will not be able to see all these frames unless your monitor supports an equally higher refresh rate.If you are recording a video with a dedicated screen capture device, it will record all the frames that are being sent from the GPU. Even if you have a monitor of 60Hz, the screen capture device will record every video data sent from the GPU.You can measure the FPS count using any FPS counter application. Some applications also have a built-in feature to display the FPS details.
Notable Differences
Both refresh rate and frame rate go hand in hand as both are responsible for displaying smooth video output.
Higher Refresh Rate or Higher Frame Rate
A higher refresh rate does provide you means to view those extra frames. However, you can benefit from a higher refresh rate monitor only if your system is giving an equal number of FPS. You will not be able to get the most out of the monitor with a higher refresh rate without adequate FPS to support it.Alternatively, if your monitor’s refresh rate is lower, but the GPU is able to provide higher frame rates, you will not see those extra frames. However, getting a higher FPS, even if you don’t have a monitor with a higher refresh rate, is always better than having lower frame rates.
Does Higher Frame Rate Mean Lower Input Latency?
In brief, yes higher frame rate does mean lower input latency. Let’s say you are working on a 60Hz monitor, but the FPS counter detects that the application is running on 144FPS. Although you will only see 60 frames in one second, the actual data sent from the GPU is 144 frames for the time interval.These frames are not displayed but they are processed by the GPU. The system does record the input even if the monitor cannot display these extra frames Hence, the perceivable output is wasted.Since the CPU has processed the information for all frames, More frames per second minimize the delay between an input command and its result on the screen. This results in input command being registered even though the display is not updated.The response will feel a little abrupt and laggy even. But the actual scenario is that the information is being processed and input data is updated.To further clarify, let us talk about a scenario where you are playing a game. Playing a game with 144FPS records your movement quite often compared to playing a game with 60FPS. Although the time difference between recording movement on higher and lower framed devices is in milliseconds, this delay might be the reason behind losing a match and winning them.Another example to further illustrate this is how your computer responds to keyboards and mice input even when the screen is powered off. The switched-off screen equivalents 0 refresh rate, but maximum FPS supported by your graphics unit. The display is not updated but the input is registered.
Can I Increase Monitor’s Refresh Rate?
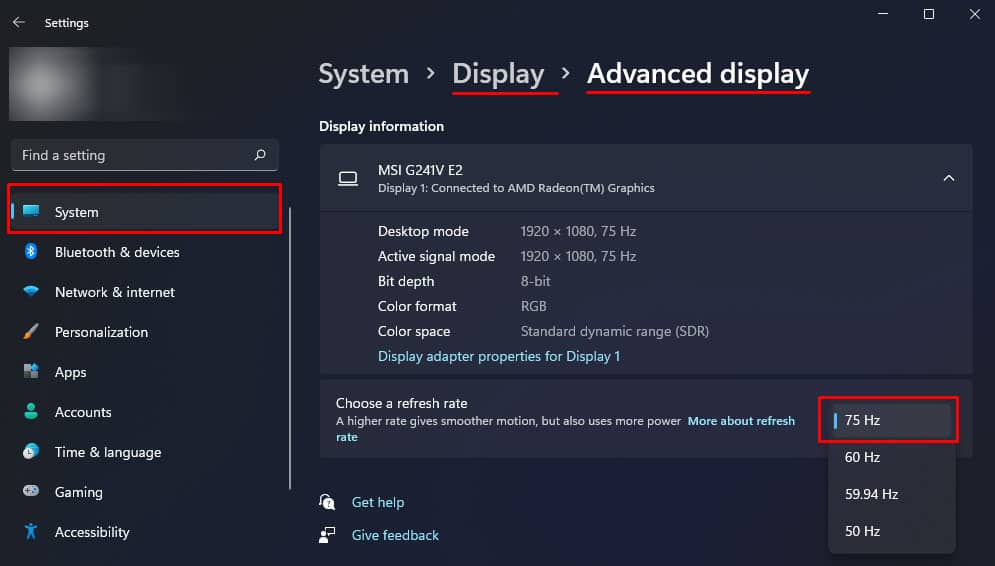
Depending on the monitor you use, you may be able to use a variable refresh rate. Gaming monitors with a higher refresh rate will most likely support overclocking. You can check if your monitor supports variable refresh rate in Display settings.