One of the easiest methods to open this tool was to right-click on the Taskbar and select Task Manager. This option is no longer available in Windows 11. However, it doesn’t mean you don’t have other options. In this article, you can find all possible ways to open the Task Manager in Windows 11.
How to Open Task Manager
There are many ways to launch this tool in Windows 11. You can pick one according to your preference.
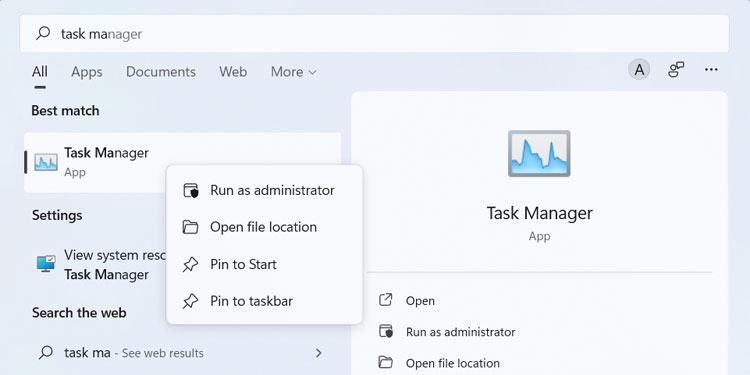
From Start Menu
You can find all your apps and features on the Start menu. To use it to open the Task Manager,Additionally, you can right-click on Task Manager and select Pin to Start or Pin to taskbar to easily access it next time.
Through Keyboard Hotkey
Using the keyboard hotkey is the easiest way to open the Task Manager. You need to press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys on your keyboard for this method.
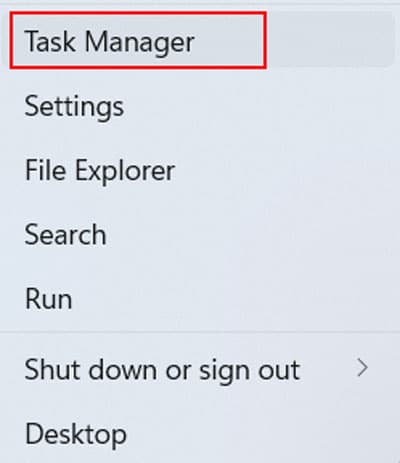
From Power User Menu
You can also open Settings from the Power User or WinX menu. Here’s how you can do so:
With CLI Command
Another easy way to launch the Task Manager is using the taskmgr command. You can enter this command on the following CLI tools:
Run (Win + R)Command PromptWindows PowerShellFile Explorer’s address bar
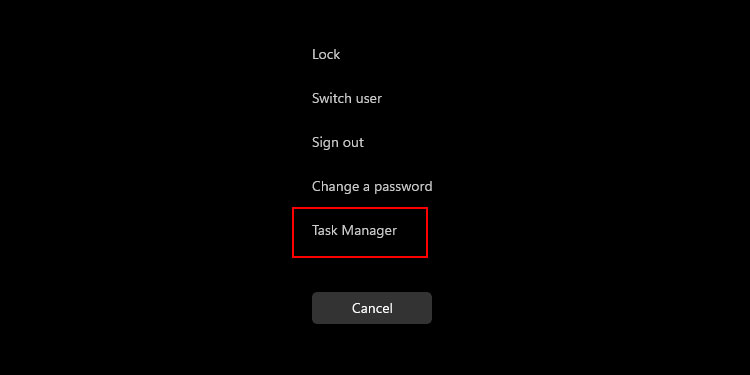
From the Ctrl + Alt + Del Screen
Pressing Ctrl + Alt + Del after logging in to an account opens up a particular screen. There are a few options you can pick, and one of them is to open the Task Manager.
From the File Explorer
You can also navigate the File Explorer to the Task Manager’s location and open it. The path is C:\Windows\System32, and the file is taskmgr.exe.
How to Use Task Manager
There are many things you can do on the Task Manager. Most users use it as a diagnostic tool to check and debug their system and application errors. Here are the details on some possible uses of this tool:
Check App Activity
The most common use of the Task Manager is to check app activity and resource utilization. In the Processes tab, you can see all your active, background, and system processes.The columns show the status and use of CPU, Memory, Power Usage, and so on for each activity. Right-clicking on a column name shows the options to show/hide possible columns.You can also check your total resource usage in detail from the Performance tab.The Details tab also shows the status of each instance of all active processes.
Check Services
The Services tab shows the status of all available services in your system. You can right-click on each and choose to Start, Stop or Restart them. You can also go to the Services app by clicking Open Services. Here, you’ll get more options for managing the services.
Start, Restart or End Tasks
Like with services, you can restart or end active tasks from the Processes tab. You can also close all the instances of the same app at once. You need to right-click on a process inside the Details tab and pick End process tree to do so. Ending tasks is very useful for closing non-responsive or background apps.You can also start a new process by clicking on File from the menu bar and selecting Run new task. Here, enter a Run command or Browse your computer to open an executable file. It also contains an option to allow admin privileges for the task.
Diagnose Processes
You can also diagnose and troubleshoot system and app errors using the Task Manager. On the Details tab, you’ll find the options to analyze the wait chain or create dump logs for each process. You can troubleshoot minor issues by analyzing the dump files.
Set App Priority
Another use of the Task Manager is to set priority for different apps. The priority level determines how much resources your system allocates to the processes.You need to right-click on a process in the Details tab and click Set priority to get the option. Keep in mind that setting priority to Realtime causes many system issues.
Enable/Disable Startup
Another important use of the Task Manager is to enable or disable Startup processes. To do so,It prevents unnecessary programs from loading automatically and speeds up your startup time.
Can’t Open Task Manager
If you can’t open the Task Manager, it’s because the tool is disabled in your system. You need to change the relevant Registry and Group Policy settings to enable it.We strongly recommend making a backup of the registry before you make any changes. Having said that, here are the steps to enable task manager via registry:If you have a domain-controlled computer, perform the above steps and then,